Solution proposal - week 4
Automatically generated from this jupyter notebook.
Solutions to exersices week 4
INF2310, spring 2017
Task 2
In this task, we will implement our own histogram function.
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_histogram(image, low=0, high=255, num_bins=255, normalized=False):
"""Simple histogram function.
This function counts the number of values in each bin. The bins are
uniform in size, and are
[low, low+bin_size), [low+bin_size), ..., [high-bin_size, high]
where
bin_size = (high - low) / num_bins.
Args:
image: n-dimensional numpy array
low: int. Smallest value included in bins
high: int. Largest value included in bins
bin_size: int. Size of bin.
normalized: bool. We assume uniform bin size, therefore if normalized == True,
sum(hist)*bin_size = 1. Otherwise hist is just the intensity frequency
in the image.
Returns:
bins: 1D numpy array. Bin values used in the histogram.
hist: 1D numpy array. Histogram values.
"""
bins = np.linspace(low, high, num_bins+1)
hist = np.zeros(num_bins, dtype='int64')
# Feel free to try different versions
for k in range(num_bins):
hist[k] = np.sum(((image >= bins[k])*(image < bins[k+1]))*1)
if k == num_bins-1:
hist[k] = np.sum(((image >= bins[k])*(image <= bins[k+1]))*1)
if normalized:
# We assume uniform bin size
bin_size = bins[1] - bins[0]
# Normalized now means that the sum of elements in the unnormalized
# histogram times the bin size should equal 1, therefore
hist = hist / (np.sum(hist) * bin_size)
# Check with numpy version
np_hist, np_bins = np.histogram(image.flatten(), bins=num_bins, range=[low, high], density=normalized)
for k, _ in enumerate(hist):
# Float comparison
assert np.isclose(hist[k], np_hist[k]), 'Something wrong in index ' + str(k)
return bins, hist
Tests
test_im = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [2, 3, 4, 5], [3, 4, 5, 6]])
bins, hist = get_histogram(test_im, 0, 10, 10, False)
print(test_im)
print(bins)
print(hist)
[[1 2 3 4]
[2 3 4 5]
[3 4 5 6]]
[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10.]
[0 1 2 3 3 2 1 0 0 0]
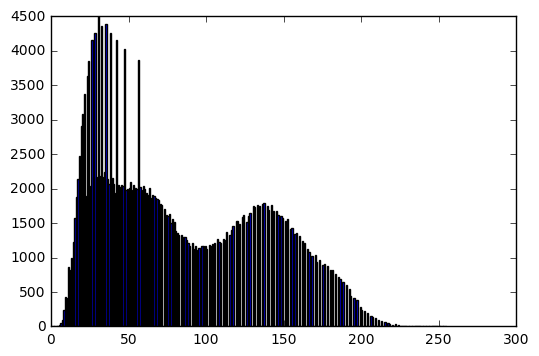
im = cv2.imread('../../assets/images/lena.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
bins, hist = get_histogram(im)
plt.figure(0)
plt.imshow(im, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure(1)
plt.bar(bins[:-1], hist)
print('Image mean: ', np.mean(im))
print('Image standard deviation: ', np.std(im))
Image mean: 124.108253479
Image standard deviation: 47.9368693516

Task 4
In this task, we shall apply a linear grayscale transform on an image such that the result image has a given mean value and standard deviation.
First, let us import an image, and display it
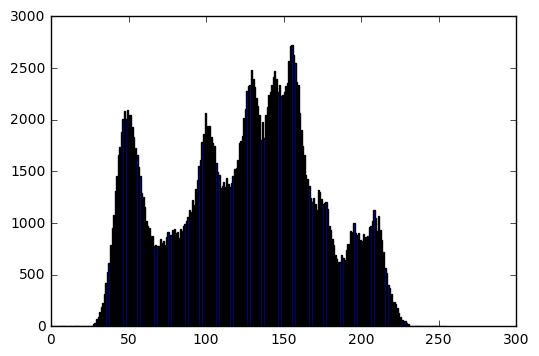
im = cv2.imread('../../assets/images/mona.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
bins, hist = get_histogram(im)
plt.figure(0)
plt.imshow(im, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure(1)
plt.bar(bins[:-1], hist)
print('Image info:')
print('Data type: ', im.dtype)
print('Min intensity value: ', im.min())
print('Max intensity value: ', im.max())
print('Mean: ', np.mean(im))
print('Standard deviation: ', np.std(im))
Image info:
Data type: uint8
Min intensity value: 27
Max intensity value: 246
Mean: 133.389663696
Standard deviation: 45.4581301793

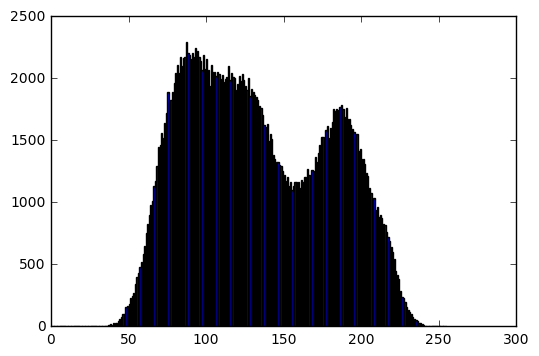
Then, we perform a linear transform
target_mean = 100
target_stddev = 20
input_mean = np.mean(im)
input_stddev = np.std(im)
scale = target_stddev / input_stddev # "a" in the lecture slides
shift = target_mean - scale*input_mean # "b" in the lecture slides
# Perform the transformation
transformed_im = shift + scale*im
# Cut the image values < 0 and > 255
transformed_im = transformed_im - transformed_im*(transformed_im < 0) - transformed_im*(transformed_im > 255)
bins, hist = get_histogram(transformed_im)
# Display result
plt.figure(0)
plt.imshow(transformed_im, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure(1)
plt.bar(bins[:-1], hist)
print('Transformed image info:')
print('Data type: ', transformed_im.dtype)
print('Min intensity value: ', transformed_im.min())
print('Max intensity value: ', transformed_im.max())
print('Mean: ', np.mean(transformed_im))
print('Standard deviation: ', np.std(transformed_im))
Transformed image info:
Data type: float64
Min intensity value: 53.1922394183
Max intensity value: 149.544640688
Mean: 100.0
Standard deviation: 20.0

Extra: A more general tranform function
Below, there is implementations of a linear transform, a logarithmic transform and a power transform.
def transform(image, which_transform, scale=1, shift=0, power=1):
"""Transforms the input image.
Args:
image: n-dimensional numpy array with values in [0, 255].
which_transform: str in {'linear', 'log', 'power'}
scale: Scaling parameter used if which_transform == 'linear'
shift: Shift parameter used if which_transform == 'linear'
power: What power to use if which_transform == 'power'.
Returns:
tr_image: numpy array with same shape as image.
"""
if which_transform == 'linear':
tr_image = shift + scale*im
# Cut values < 0 and > 255
tr_image = tr_image - tr_image*(tr_image < 0) - tr_image*(tr_image > 255)
elif which_transform == 'log':
# This is such that intensity value 0 is mapped to 0, and intensity value
# 255 is mapped to 255.
c = 255 / np.log(256)
tr_image = c * np.log(image.astype(np.float) + 1)
elif which_transform == 'power':
# This is such that intensity value 0 is mapped to 0, and intensity value
# 255 is mapped to 255.
c = 255 / (255**power)
tr_image = c * (im.astype(np.float)**power)
else:
print('Transform {} is not implemented yet'.forma(which_transform))
tr_image = np.zeros_like(image)
return np.round(tr_image).astype('uint8')
Linear transform
target_mean = 100
target_stddev = 20
input_mean = np.mean(im)
input_stddev = np.std(im)
scale = target_stddev / input_stddev # "a" in the lecture slides
shift = target_mean - scale*input_mean # "b" in the lecture slides
transformed_im = transform(im, which_transform='linear', scale=scale, shift=shift)
bins, hist = get_histogram(transformed_im)
# Display result
plt.figure(0)
plt.imshow(transformed_im, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure(1)
plt.bar(bins[:-1], hist)
print('Transformed image info:')
print('Data type: ', transformed_im.dtype)
print('Min intensity value: ', transformed_im.min())
print('Max intensity value: ', transformed_im.max())
print('Mean: ', np.mean(transformed_im))
print('Standard deviation: ', np.std(transformed_im))
Transformed image info:
Data type: uint8
Min intensity value: 53
Max intensity value: 150
Mean: 100.010593414
Standard deviation: 20.0034103902

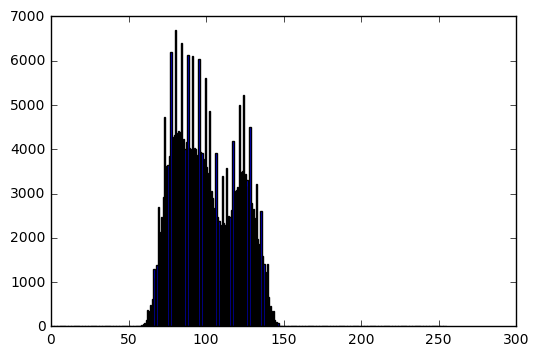
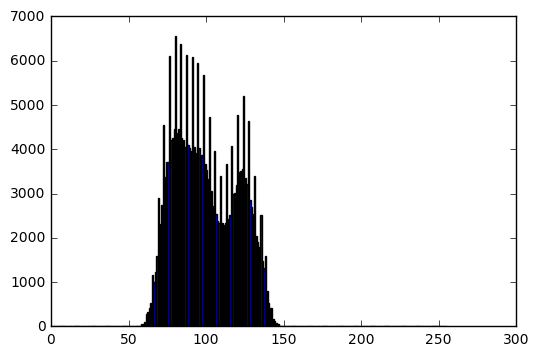
Logarithmic transform
transformed_im = transform(im, which_transform='log')
bins, hist = get_histogram(transformed_im)
# Display result
plt.figure(0)
plt.imshow(transformed_im, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure(1)
plt.bar(bins[:-1], hist)
print('Transformed image info:')
print('Data type: ', transformed_im.dtype)
print('Min intensity value: ', transformed_im.min())
print('Max intensity value: ', transformed_im.max())
print('Mean: ', np.mean(transformed_im))
print('Standard deviation: ', np.std(transformed_im))
Transformed image info:
Data type: uint8
Min intensity value: 153
Max intensity value: 253
Mean: 222.567173004
Standard deviation: 16.4205089579

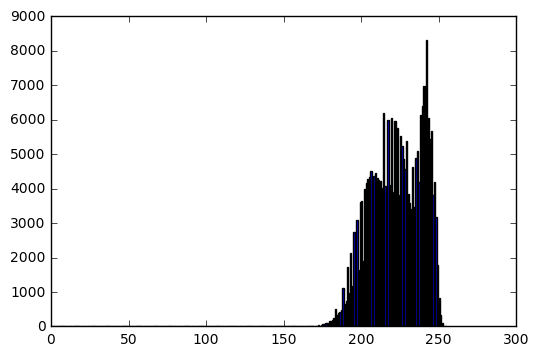
Power transform
transformed_im = transform(im, which_transform='power', power=2)
bins, hist = get_histogram(transformed_im)
# Display result
plt.figure(0)
plt.imshow(transformed_im, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.axis('off')
plt.figure(1)
plt.bar(bins[:-1], hist)
print('Transformed image info:')
print('Data type: ', transformed_im.dtype)
print('Min intensity value: ', transformed_im.min())
print('Max intensity value: ', transformed_im.max())
print('Mean: ', np.mean(transformed_im))
print('Standard deviation: ', np.std(transformed_im))
Transformed image info:
Data type: uint8
Min intensity value: 3
Max intensity value: 237
Mean: 77.8498153687
Standard deviation: 49.9954186908